Is Hydronium A Lewis Acid
This polyatomic ion is the hydronium ion and forms whenever a strong acid is added to water. 56 to 25 3.

1 Theories Of Acids And Bases A Arrhenius Theory Chegg Com
We have seen an introductory definition of an acid.

Is hydronium a lewis acid. 42 to 82 d. A substance that ionizes in water and increases the number of. A Lewis acid named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N.
Hydroxide attacks and accepts the H from hydronium. Here the oxygen atom donates an electron pair to the proton forming a coordinate covalent bond in the process. To be a Lewis acid the molecule or ion should possess a vacant orbital or a π-bond in which it can accept a lone electron pair.
Hydronium breaks up to yield an H in solution. Ce2H3O S2O32- - H2S2O3 2 H2Otag1 The acid is the species that donates the transferred proton the base is the species that accepts it. Although alcohols and amines can be BrønstedLowry acids they can also function as Lewis bases due to the lone pairs of electrons on their oxygen and nitrogen atoms.
Hydronium ions are acids according to all three definitions. When the hydronium ion solution is increased to twice the original concentration the change in pH could be from. A compound that donates a proton a hydrogen ion H to another compound is called a Brønsted-Lowry acid and a Lewis acid is any species that can accept a pair of electrons.
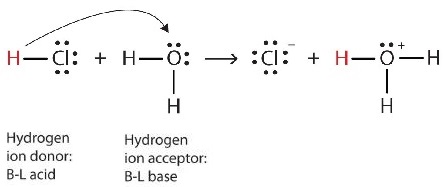
An acid is a compound that reacts with water and increases the amount of hydronium ion present. An acid solution doesnt mean it is only hydronium ion solution because acid can be bronsted acid can be arhenius acid or it can be Lewis acid. To re-cap the Lewis structures for H 2 O HCl H 3 O and Cl are drawn to show what happens to the electrons when a strong acid like HCl g is added to water in the reaction.
Defined acids and bases as acid a substance that ionizes in water and increases the number of hydrogen ions H and Base. The resulting Lewis acid has a 1 charge associated with it. 38 to 35 b.
Follow edited Aug 5 14 at 1610. The chloride anion Cl forms an ionic bond with the hydronium cation. The H on Hydronium accepts the attacking electron pair to form a bond.
23 to 26 c. No H3O is not a Lewis acid. Which of the following is considered as a Lewis acid but not a Bronsted-Lowry acid.
Suppose aqueous HCl solution has hydronium ion thus you can tell it acid. HSC Chemistry Acidic EnvironmentCatfish Ed Catfish education Whiting Mr Whiting Mr P Whiting Whiting Sc. The first step a reaction of hydronium ceH3O with thiosulfate ceS2O32- has to be an acid-base reaction because that is practically the only reaction hydronium undergoes.
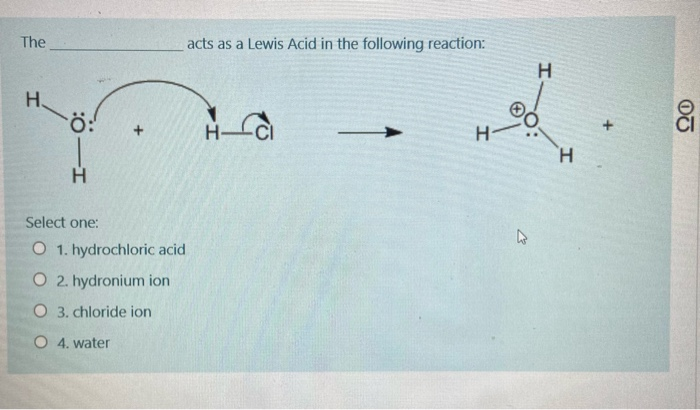
In the chapter on acids and bases we saw two more definitions of acids. Because according to Lewis concept of acid-base lone electron pair acceptors are Lewis acids. The H ion acts as a Lewis acid and H 2 O acts as a Lewis base.
Arrhenius Acid Definition. Lewis is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adductA Lewis base then is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis. Complex ions are examples of Lewis acid-base adducts and comprise central metal atoms or ions acting as Lewis acids bonded to molecules or ions called ligands that act as Lewis bases.
A Lewis acid is a species that can accept an electron pair whereas a Lewis base has an electron pair available for donation to a Lewis acid. What is the main difference between the 3 acid base theories. Acids and bases are an important part of organic chemistry.
A Lewis acid is a species that can accept an electron pair whereas a Lewis base has an electron pair available for donation to a Lewis acid. Alkoxide ion is a strong conjugate base which shows that alcohols are weak acid but alcohols are strong lewis bases and donate electrons to hydrogen in reaction with HX. Here no hydronium ion present but it is acid and they are lewis acidAcid.
Lewis acids bases electrophiles nucleophiles. Hydronium Ion Formation and Lewis Dot Structure. Complex ions are examples of Lewis acid-base adducts and comprise central metal atoms or ions acting as Lewis acids bonded to molecules or ions called ligands that act as Lewis bases.
Although the hydronium ion is the nominal Lewis acid here it does not itself accept an electron pair but acts merely as the source of the proton that coordinates with the Lewis base. The reaction between the water molecule and the proton yields a hydronium ion H 3 O as illustrated below. The point about the electron-pair remaining on the donor species is especially important to bear in mind.
One of the most applicable theories is the Lewis acidbase motif that extends beyond the Br ø nsted-Lowry definition described in the previous section. Now take BF3 BCl3 or AlCl3.

Lewis Acids And Bases Chemistry Atoms First

Lewis Acid And Base Definitions With Examples
1 12 Bronsted Lowry Acids And Bases Review Chemistry Libretexts
What Are The Two Conditions For The Formation Of Hydronium Ion Quora

Lewis Acids And Bases Definition Properties Reactions Uses

Lewis Acids And Bases Chemistry Atoms First

Defining Acids And Conjugate Acid Base Pairs Villanova College Chemistry Blog
Ti Ch 3 Acids And Bases 22 Of 33 Pe Q3 22 Which Chegg Com

Lewis Acids And Bases Definition Properties Reactions Uses

Chemistry Chemical Bonding 22 Of 35 Lewis Structures For Ions Hydronium Ion H3o Youtube

10 3 Molecular Definitions Of Acids And Bases Chemistry Libretexts

The Chemistry Of Acids And Bases Some Properties Of Acids Th Produce H As H 3 O Ions In Water The Hydronium Ion Is A Hydrogen Ion Attached To Ppt Download
Acid Definitions Lewis Acid Brnstedlowry Arrhenius Acids Arrhenius

Lewis Acids Bases Lewis Acid A Substance That
The Acts As A Lewis Acid In The Following Reaction Chegg Com
